Deciphering the Language of Jewelry: A Comprehensive Guide to Hallmarks
Related Articles: Deciphering the Language of Jewelry: A Comprehensive Guide to Hallmarks
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Deciphering the Language of Jewelry: A Comprehensive Guide to Hallmarks. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Deciphering the Language of Jewelry: A Comprehensive Guide to Hallmarks

Hallmarks, those tiny, often inconspicuous markings found on jewelry, hold a wealth of information about the piece’s origin, composition, and even its historical significance. While they may appear as mere scratches or engravings, these marks serve as a vital language, revealing the story behind the precious metal.
Understanding the Importance of Hallmarks
Hallmarks are not merely decorative elements. They serve a crucial purpose:
- Guaranteeing Quality and Purity: Hallmarks act as a guarantee of the metal’s purity, ensuring that the jewelry is made from genuine and legally defined standards of precious metal.
- Protecting Consumers: They shield consumers from fraudulent practices by providing a verifiable record of the metal’s quality, preventing the sale of counterfeit or substandard pieces.
- Tracing History and Origin: Hallmarks can pinpoint the origin of the jewelry, often revealing the country or city where it was crafted, and even the specific workshop or maker.
- Determining Age and Value: Hallmarks can be used to date the jewelry, providing valuable information about its age and historical context, which can significantly impact its monetary value.
The Evolution of Hallmarks
The practice of hallmarking dates back centuries, evolving alongside the craftsmanship of jewelry making.
- Early Hallmarks: Some of the earliest recorded hallmarks were used in ancient Rome, where goldsmiths applied their personal marks to ensure accountability and identify their work.
- Medieval Guilds: During the Middle Ages, guilds of goldsmiths in Europe began using hallmarks to regulate the quality of their work and protect their reputation.
- National Standardization: As trade expanded and international markets grew, national hallmarking systems emerged, standardizing the use of hallmarks and establishing a consistent system for identifying the purity and origin of precious metals.
Decoding the Language of Hallmarks
Hallmarks are a visual language, each mark carrying specific information. Understanding the components of a hallmark is essential to deciphering its meaning:
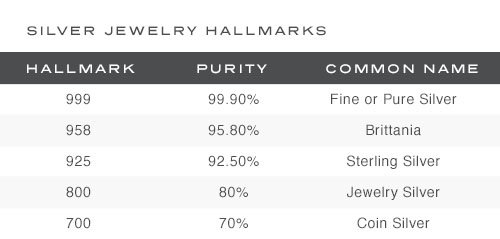
- Metal Purity Mark: This mark indicates the fineness or purity of the precious metal, often expressed as a number, fraction, or symbol. For example, "925" signifies sterling silver (92.5% silver and 7.5% other metals), "18K" denotes 18 karat gold (75% gold and 25% other metals), and "Pt950" represents platinum with 95% purity.
- Assay Office Mark: This mark represents the location where the piece was assayed and hallmarked. Assay offices are official institutions responsible for testing and certifying the purity of precious metals. Each office has its unique hallmark, often incorporating local symbols or initials.
- Maker’s Mark: This mark is a unique identifier of the individual craftsman, workshop, or company that created the piece. It can be a letter, initials, a symbol, or a logo, providing a direct link to the origin of the jewelry.
- Date Letter: Some hallmarking systems include a date letter, indicating the year in which the piece was assayed and marked. This letter usually changes annually, allowing for precise dating of the jewelry.
Navigating the World of Hallmarks: A Comprehensive Guide
The specific information conveyed by a hallmark varies depending on the country and historical period of its origin. Here is a brief overview of hallmarking systems around the world:
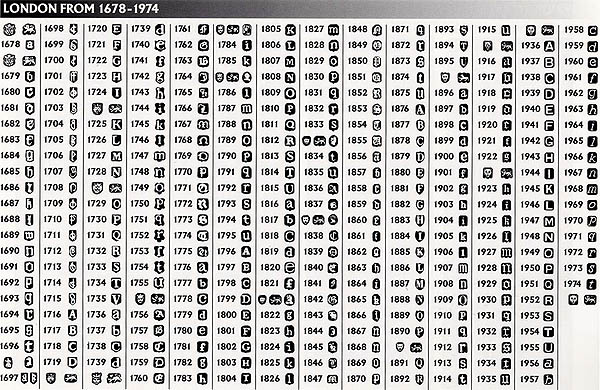
United Kingdom: The United Kingdom boasts one of the oldest and most comprehensive hallmarking systems. Hallmarks typically include the metal purity mark, the assay office mark, the maker’s mark, and the date letter.
United States: While the United States does not have a mandatory national hallmarking system, some states have their own regulations. However, most American jewelry is marked with the metal purity mark, such as "14K," "18K," or "925," along with the maker’s mark.
European Union: The European Union has standardized hallmarking regulations, requiring all jewelry to be marked with the metal purity mark, the assay office mark, and the maker’s mark. The specific format and design of the hallmarks may vary depending on the individual member state.
Canada: Canada follows a similar hallmarking system to the United Kingdom, requiring the metal purity mark, the assay office mark, the maker’s mark, and the date letter.
Australia: Australian hallmarking regulations require the metal purity mark, the assay office mark, and the maker’s mark.
Japan: Japan has a unique hallmarking system, with the metal purity mark, the assay office mark, and a special mark indicating the year of manufacture.
India: India follows a system of compulsory hallmarking, requiring all gold jewelry to be marked with the metal purity mark, the assay office mark, and the maker’s mark.
China: China has a national hallmarking system, with the metal purity mark, the assay office mark, and the maker’s mark.
Understanding Hallmark Systems: A Deeper Dive
-
British Hallmarks: The British hallmarking system is highly regarded for its historical significance and comprehensive nature. It includes a wide range of marks, each carrying specific information about the jewelry.
- Assay Office Marks: The UK has several assay offices, each with its unique mark. The most prominent ones are the London Assay Office (the oldest in the UK), the Birmingham Assay Office, the Sheffield Assay Office, and the Edinburgh Assay Office.
- Date Letters: The British hallmarking system utilizes a system of date letters, which change annually. By deciphering the date letter, one can determine the year in which the piece was hallmarked.
- Additional Marks: British hallmarks can also include additional marks, such as the "Lion Passant" mark (indicating sterling silver), the "Crown" mark (indicating gold), or the "Leopard’s Head" mark (indicating platinum).
-
American Hallmarks: While the United States does not have a mandatory national hallmarking system, some states, such as California and New York, have their own regulations. The most common hallmark found on American jewelry is the metal purity mark, such as "14K," "18K," or "925."
- State Regulations: States that have hallmarking regulations often require the maker’s mark, along with the metal purity mark.
- Federal Regulations: The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) has regulations regarding the use of precious metal marks, ensuring accurate labeling and consumer protection.
-
European Union Hallmarks: The European Union has standardized hallmarking regulations, requiring all jewelry to be marked with the metal purity mark, the assay office mark, and the maker’s mark.
- Assay Office Marks: Each member state of the EU has its own assay office, which uses a unique mark. The assay office mark typically includes the country’s initials or a symbol representing the city or region.
- Metal Purity Marks: The metal purity mark is standardized across the EU, using the same symbols and numbers to indicate the fineness of the precious metal.
The Importance of Expert Authentication
While this guide provides a comprehensive overview of hallmarks, it is essential to note that accurate interpretation requires expertise.
- Professional Appraisers: Professional appraisers or gemologists with specialized knowledge in hallmarking can accurately identify and interpret the markings on jewelry, providing valuable insights into its authenticity, age, and value.
- Online Resources: Numerous online resources, such as databases of hallmarking systems and websites dedicated to jewelry identification, can provide valuable information. However, it is important to use reputable sources and exercise caution when relying solely on online information.
FAQs: Hallmarks on Jewelry
Q: What is the purpose of hallmarks on jewelry?
A: Hallmarks serve several purposes:
- Guaranteeing Metal Purity: They ensure the jewelry is made from genuine and legally defined standards of precious metal.
- Protecting Consumers: They prevent fraudulent practices by providing a verifiable record of the metal’s quality.
- Tracing History and Origin: They pinpoint the origin of the jewelry, revealing the country or city where it was crafted.
- Determining Age and Value: They can be used to date the jewelry, providing valuable information about its age and historical context.
Q: Are hallmarks mandatory on all jewelry?
A: The requirement for hallmarks varies depending on the country and its specific regulations. Some countries have mandatory hallmarking systems, while others do not.
Q: Can I decipher hallmarks on my own?
A: While this guide provides a general overview, accurate interpretation requires expertise. It is recommended to consult with a professional appraiser or gemologist for accurate identification.
Q: What should I look for when examining hallmarks?
A: Look for the following components:
- Metal Purity Mark: This mark indicates the fineness of the precious metal.
- Assay Office Mark: This mark identifies the location where the piece was assayed and hallmarked.
- Maker’s Mark: This mark is a unique identifier of the craftsman, workshop, or company that created the piece.
- Date Letter: Some hallmarking systems include a date letter, indicating the year in which the piece was assayed and marked.
Q: What if my jewelry doesn’t have any hallmarks?
A: The absence of hallmarks does not necessarily indicate that the jewelry is fake. Some countries may not have mandatory hallmarking systems, or the marks may have worn off over time. It is recommended to seek professional appraisal for accurate identification.
Tips: Hallmarks on Jewelry
- Observe Carefully: Examine the jewelry closely for any markings, even small or faint engravings.
- Research Hallmarks: Use online resources or consult with a professional appraiser to research the specific hallmarking system of the jewelry’s origin.
- Compare with Known Examples: If possible, compare the hallmarks on your jewelry with known examples or images of authentic hallmarks.
- Consider the Historical Context: The age and style of the jewelry can provide clues about its potential hallmarking system.
- Consult with Professionals: For accurate identification and interpretation, consult with a professional appraiser or gemologist specializing in hallmarking.
Conclusion
Hallmarks are a crucial element in understanding the history, authenticity, and value of jewelry. They provide a tangible connection to the craftsmanship, origin, and quality of the piece. By understanding the language of hallmarks, collectors, enthusiasts, and buyers can gain valuable insights into the world of precious metals and the stories they hold. Whether you are a seasoned collector or a curious novice, exploring the fascinating world of hallmarks can enhance your appreciation for the art and craft of jewelry making.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering the Language of Jewelry: A Comprehensive Guide to Hallmarks. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!