Navigating the Australian Import Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Navigating the Australian Import Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Australian Import Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Australian Import Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide
Importing goods into Australia presents a unique set of challenges and opportunities. While the process might seem daunting, understanding the intricacies of Australian import regulations and procedures can pave the way for successful business ventures and access to a vast market. This comprehensive guide aims to provide a detailed overview of the import process, equipping importers with the necessary knowledge to navigate the Australian landscape effectively.
Understanding the Importance of Imports
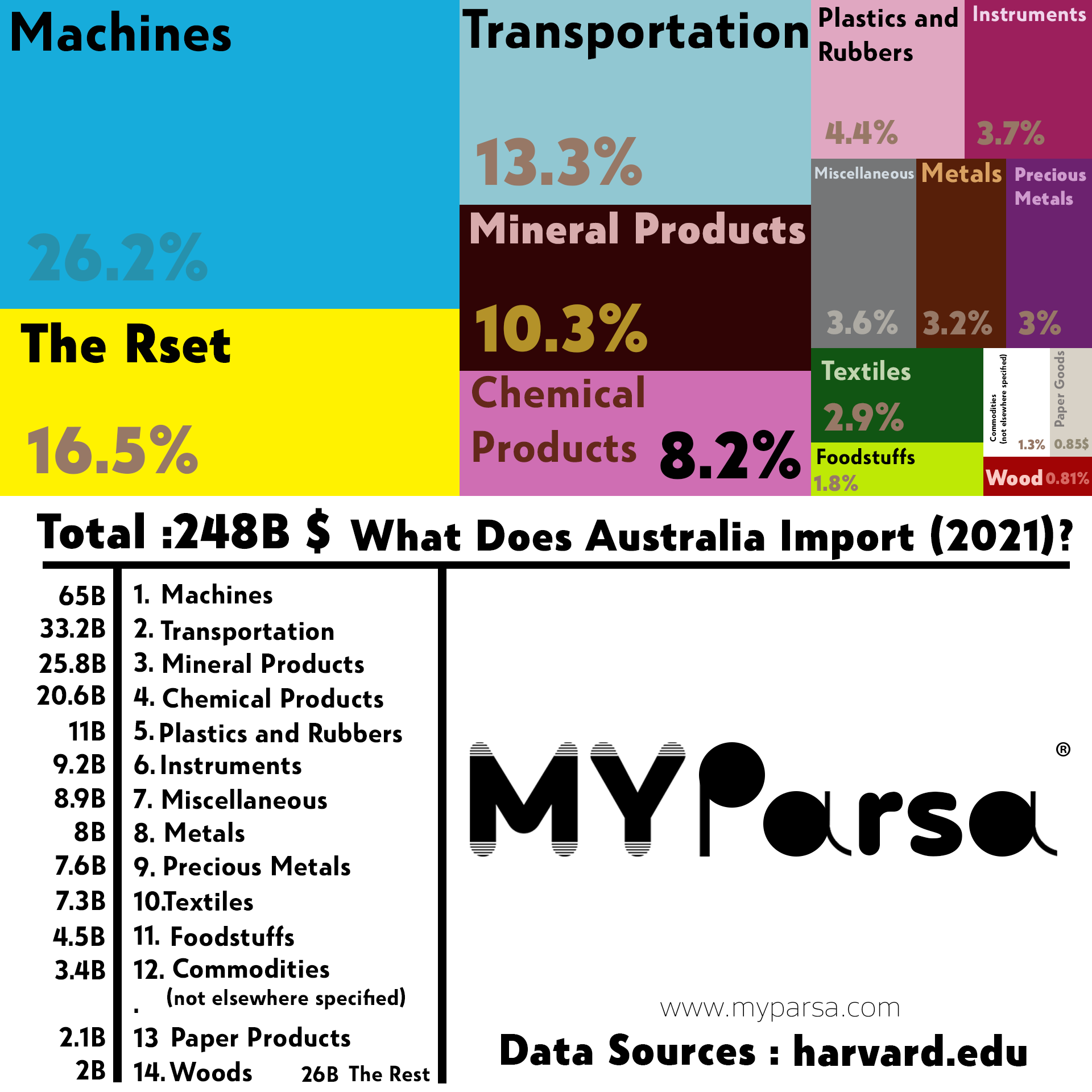
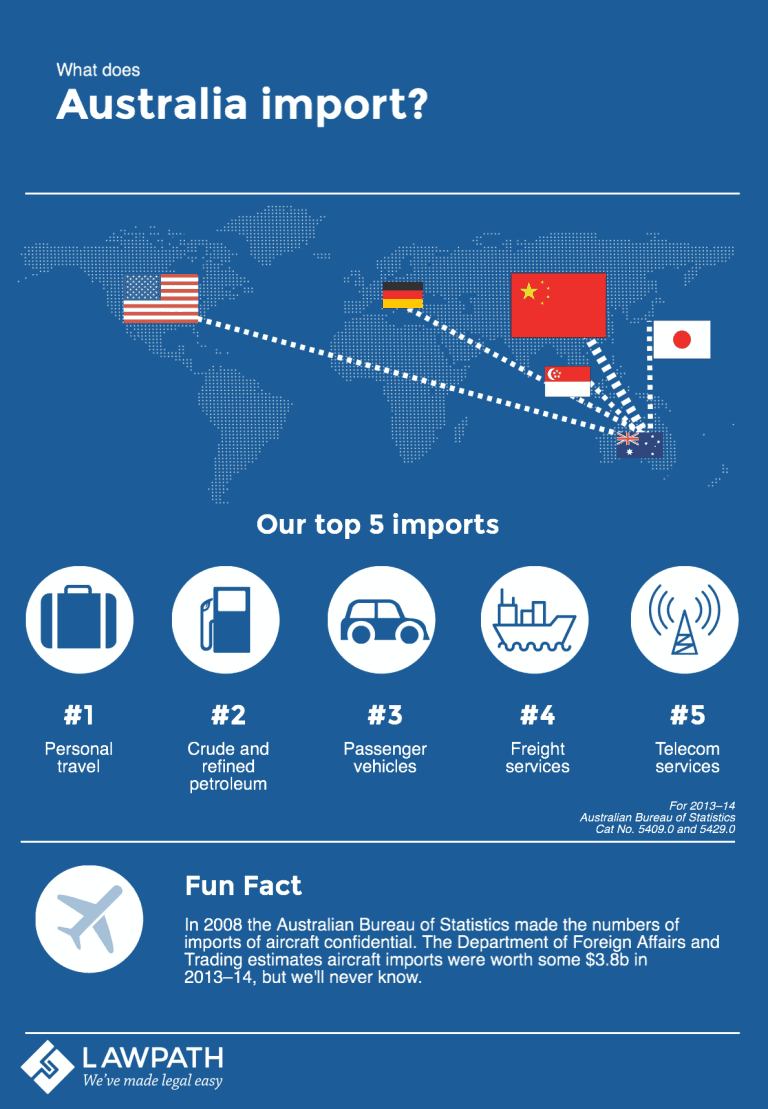
Australia, with its diverse economy and thriving consumer market, heavily relies on imports to meet the demands of its population. The country imports a wide range of goods, from essential commodities like fuel and food to manufactured products, technology, and luxury items. Imports play a crucial role in:
- Providing access to goods not readily available domestically: Australia’s unique geographic location limits its domestic production capabilities for certain goods. Imports bridge this gap, ensuring access to a wider variety of products for consumers and businesses.
- Boosting competition and driving down prices: Imports introduce competition into the domestic market, leading to price reductions and improved product quality. This benefits consumers by offering greater choice and affordability.
- Supporting economic growth and employment: Imports contribute to economic growth by providing essential raw materials and intermediate goods for local industries. They also support employment in sectors related to import activities, such as logistics, warehousing, and customs brokerage.
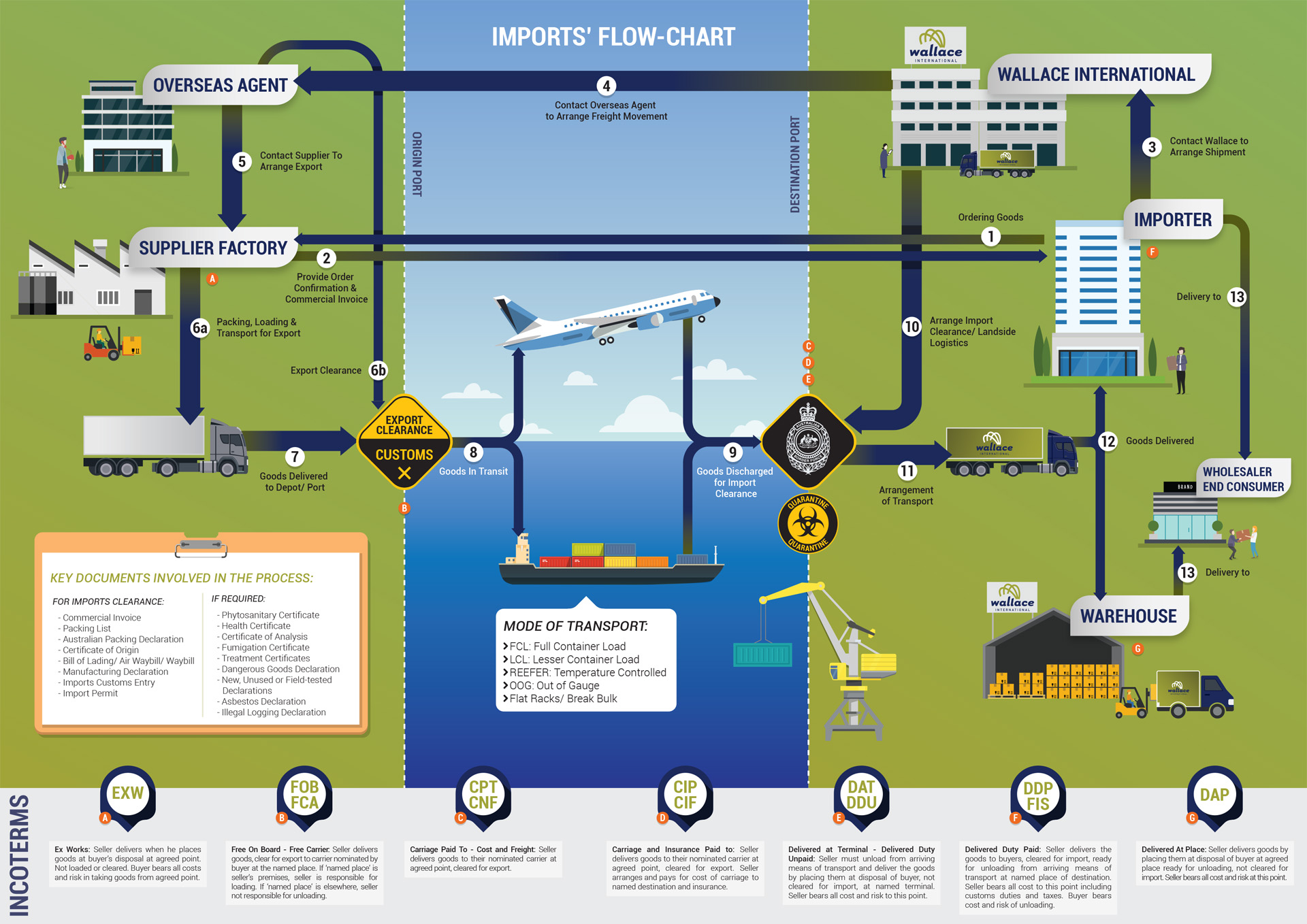
Navigating the Import Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
Importing into Australia requires a systematic approach, involving multiple steps and stakeholders. The following guide provides a comprehensive overview of the key stages involved:
1. Research and Planning
- Identify the product: Clearly define the goods you intend to import, including their specific characteristics, quantity, and intended use.
- Market research: Conduct thorough market research to assess the demand for your product in Australia. Analyze competitor offerings, pricing strategies, and potential customer base.
-
Determine import regulations: Research the specific import regulations for your product category. This involves understanding:
- Tariff classifications: The Australian Customs Tariff (ACT) categorizes imported goods based on their characteristics and purpose.
- Prohibited and restricted goods: Certain goods are prohibited or restricted from entry into Australia due to safety, health, or environmental concerns.
- Licensing requirements: Specific licenses or permits may be required for certain product categories, such as pharmaceuticals, agricultural products, or hazardous materials.
- Quality standards: Australia has stringent quality standards for imported goods, ensuring compliance with safety and regulatory requirements.
- Identify potential suppliers: Research and evaluate potential suppliers based on factors such as product quality, reliability, pricing, and shipping capabilities.
- Estimate costs: Calculate the total cost of importing, including product cost, shipping fees, insurance, customs duties, taxes, and any other related expenses.
2. Sourcing and Procurement
- Negotiate contracts: Once you have identified a suitable supplier, negotiate a comprehensive contract that outlines all terms and conditions, including payment terms, delivery schedules, and quality specifications.
- Arrange payment: Determine the preferred payment method, such as letter of credit, wire transfer, or other secure payment options.
- Ensure product quality: Establish clear quality control procedures to ensure that the imported goods meet Australian standards and specifications.
3. Shipping and Logistics
- Choose a shipping method: Select the most appropriate shipping method based on factors such as cost, transit time, and product characteristics. Options include sea freight, air freight, or courier services.
-
Prepare shipping documentation: Prepare all necessary shipping documents, including:
- Bill of lading: A document acknowledging receipt of goods for shipment.
- Commercial invoice: A document detailing the goods being shipped, their value, and the seller and buyer information.
- Packing list: A detailed list of the goods contained in each shipping container.
- Certificate of origin: A document certifying the origin of the goods.
- Arrange insurance: Obtain adequate insurance coverage to protect your goods against damage or loss during transit.
4. Customs Clearance
- Prepare import declaration: Complete the necessary import declaration forms, providing detailed information about the imported goods and their value.
- Submit documentation: Submit the completed import declaration and supporting documentation to the Australian Border Force (ABF) for clearance.
- Pay customs duties and taxes: Calculate and pay any applicable customs duties and taxes based on the goods’ tariff classification and value.
- Inspect goods: The ABF may conduct inspections of the imported goods to verify their compliance with Australian regulations.
5. Delivery and Distribution
- Arrange delivery: Coordinate with a freight forwarder or logistics provider to arrange the delivery of the goods to your designated location in Australia.
- Distribute goods: Manage the distribution of the imported goods to your customers or retail outlets.
FAQs Regarding Importing into Australia
1. What are the key considerations for importing into Australia?
Key considerations include:
- Understanding Australian import regulations: This involves research on tariff classifications, prohibited and restricted goods, licensing requirements, and quality standards.
- Identifying reliable suppliers: Choosing suppliers with a proven track record of quality and reliability is crucial.
- Estimating costs: Accurately calculating all costs associated with importing, including shipping, customs duties, and taxes, is essential for financial planning.
2. What are the most common challenges faced by importers?
Challenges include:
- Navigating complex regulations: The Australian import process involves multiple regulations and procedures that can be challenging to understand and navigate.
- Managing costs: Importing goods can be expensive, and managing costs effectively is crucial for profitability.
- Ensuring product quality: Meeting Australian quality standards can be demanding, requiring stringent quality control measures.
- Dealing with delays: Delays in shipping, customs clearance, or logistics can disrupt supply chains and impact business operations.
3. What resources are available to assist importers?
Resources include:
- Australian Border Force (ABF): The ABF provides comprehensive information on import regulations, procedures, and resources for importers.
- Department of Agriculture, Water and the Environment (DAWE): The DAWE manages import regulations for agricultural products, ensuring biosecurity and food safety.
- Australian Trade and Investment Commission (Austrade): Austrade provides support and guidance to Australian businesses involved in international trade, including importing.
- Industry associations: Various industry associations provide specific guidance and support for importers in particular sectors.
4. What tips can help importers succeed?
- Start early: Begin the import process well in advance to allow ample time for research, planning, and documentation.
- Seek professional advice: Consult with customs brokers, freight forwarders, and other industry experts to ensure compliance and efficiency.
- Build strong relationships: Establish strong relationships with suppliers, logistics providers, and customs brokers to facilitate smooth operations.
- Stay informed: Keep abreast of changes in import regulations and industry best practices to maintain compliance and optimize import processes.
Conclusion
Importing into Australia presents both challenges and opportunities for businesses. By understanding the intricacies of the import process, conducting thorough research, and seeking professional guidance, importers can navigate the Australian landscape effectively and access the benefits of this vast market. With careful planning, strategic partnerships, and compliance with regulations, importing can become a viable and profitable venture, contributing to economic growth and providing access to a wide range of goods for Australian consumers and businesses.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Australian Import Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!